Mussels
Mussels are known scientifically as Mytilidae. They are a mollusc belonging to the family of bivalves that live very deep in coastal waters. They are found all over the world.
The principal area for cultivation of mussels in Catalonia is the Ebro Delta.

-
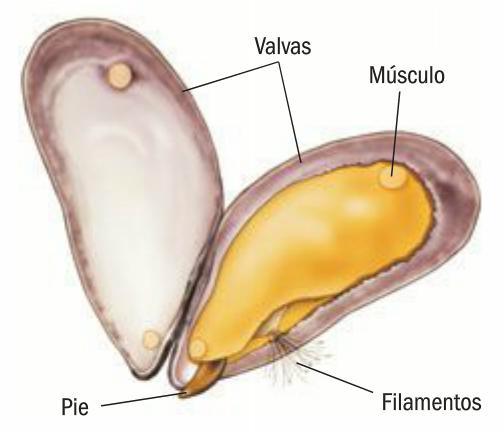
Mussels consist of a shell, which has three layers: prismatic layer, iridescent nacre layer and periostracum layer. There are a further two valves that protect the flesh. Finally, there is the foot, which secretes a slimy substance, called byssus, which allows it to cling to rocks.
-
The best time of the year to eat them is between April and May. In summer, between June and September, they can also be found and are good to eat, however, in theory, this is when this animal reproduces.
-
The most important thing is to look at whether the mussel is closed or if the shell is broken. That way we will know if it is fresh and if it is in good condition.
-
They should be kept closed and they should not be dried out, keeping them moist with a cloth or a newspaper or kitchen paper. They can also be kept in the bag or net bag in which they have been bought (if it is a bag, holes should be made).
In the fridge, they should be kept in the least cold part which is normally the vegetable drawer in order to avoid any freezing so that they can open later. For this same reason, if you do want to freeze them, they should first be cooked.
Shellfish can be kept in the fridge for 2 to 3 days, at the most.
-
Mussels are rich in amino acids with high nutritional value. They are low in sugars and do not contain fat or fibre. Although they are rich in cholesterol, this is blocked by fitosterols from the phytoplankton which they eat. It should also be noted that they are rich in potassium (which has a diuretic effect), phosphorus, sodium, calcium, iron, zinc, vitamin A, B and B12, and folic acid.
Mussels maintain their allergen properties both when eaten cooked or raw. Normally an allergy develops in adulthood and is identified by the appearance of hives, or inflammation in certain areas of the body (normally the digestive system).
-
- Fried: with lots of olive oil, battered or in tempura.
- Sautéed: as part of a stew, with onion and tomato.
- In a cream: boiled and stewed with cream.
- Pickled: to preserve them between seasons, with oil and vinegar.
- Steamed: simply opened and with a little bit of lemon.
- With rice: as part of another dish.










